
In the steel industry, operating under harsh conditions such as extreme temperatures and heavy loads, efficient and safe material handling is paramount. One of the most common challenges procurement and technical teams encounter is the risk of equipment failure and worker injury during the transportation of hot steel plates in continuous casting processes. This often causes costly downtime and compromised safety.
High-efficiency power-driven steel plate clamps are engineered specifically for the brutal demands of continuous casting steel handling. Built with high-strength alloy steel, these clamps combine durability with precision. Their advanced hydraulic drive mechanism ensures a firm yet controlled grip, minimizing risks of slippage during transport.
| Feature | Benefit | Impact on Operations |
|---|---|---|
| High-Strength Alloy Steel Material | Superior wear and heat resistance | Extended service life under continuous casting heat up to 1,200°C |
| Hydraulic Drive Mechanism | Consistent grip force with adjustable pressure | Reduced risk of steel plate drop, enhancing operator safety |
| Automatic Open-Close Function | Precision handling and faster cycle times | Improved throughput by up to 15% in typical hot mill operations |
The heart of these clamps lies in their hydraulic system, which provides consistent pressure control tailored to the plate’s thickness and surface condition. This precision is critical — too much force can damage the steel plate's surface, while too little risks slippage. The automatic open-close feature, integrated with sensors, delivers seamless operation reducing operator intervention, thus minimizing human error and injury risks.
For example, a major steel producer in Eastern Europe reduced clamp-related accidents by 40% within six months after retrofitting their hot rolling lines with these hydraulic clamps.
In a recent deployment at a leading hot-rolled steel plant in South Korea, integrating these clamps into the continuous casting line resulted in consistent plate handling with zero downtime attributed to clamp failures over a 12-month period. Their ability to withstand temperature spikes of up to 1,200°C without degradation significantly improved production continuity.
Similarly, a logistics center specializing in steel transportation across Southeast Asia adopted the clamps’ hydraulic open-close automation, reporting a 20% uplift in operational efficiency due to faster plate transfers and reduced labor-dependent errors.
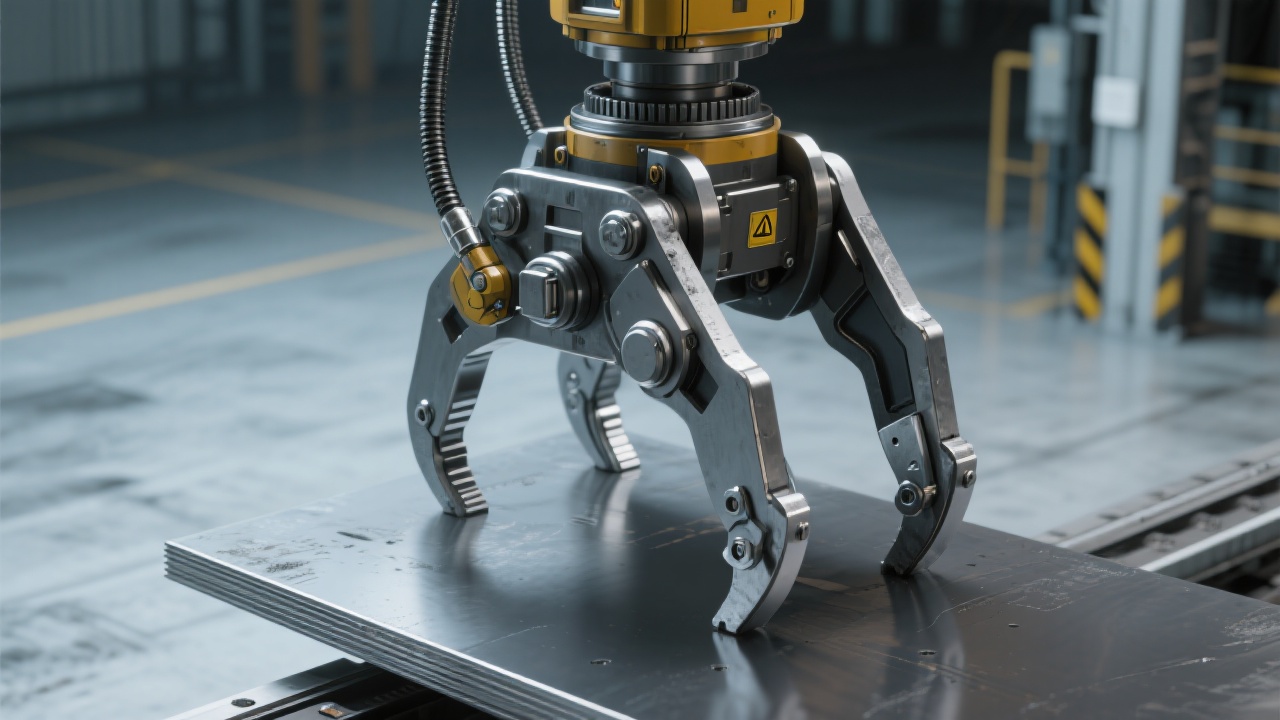
Proper maintenance of these hydraulic clamps is essential to sustain their performance. Given the exposure to abrasive dust, high humidity, and thermal cycling, daily inspections should focus on hydraulic fluid levels, cylinder seals, and clamping jaw wear.
Regular lubrication schedules and pre-shift functionality tests can prevent up to 70% of unexpected failures, keeping operational costs down and safeguarding workplace safety.
The steel industry's high throughput demands and safety regulations require equipment that marries strength and intelligence. Power-driven steel plate clamps meet these needs by ensuring consistent gripping force, with adaptability for differing load profiles and steel grades. They are indispensable in environments where manual handling risks both quality and personnel safety.
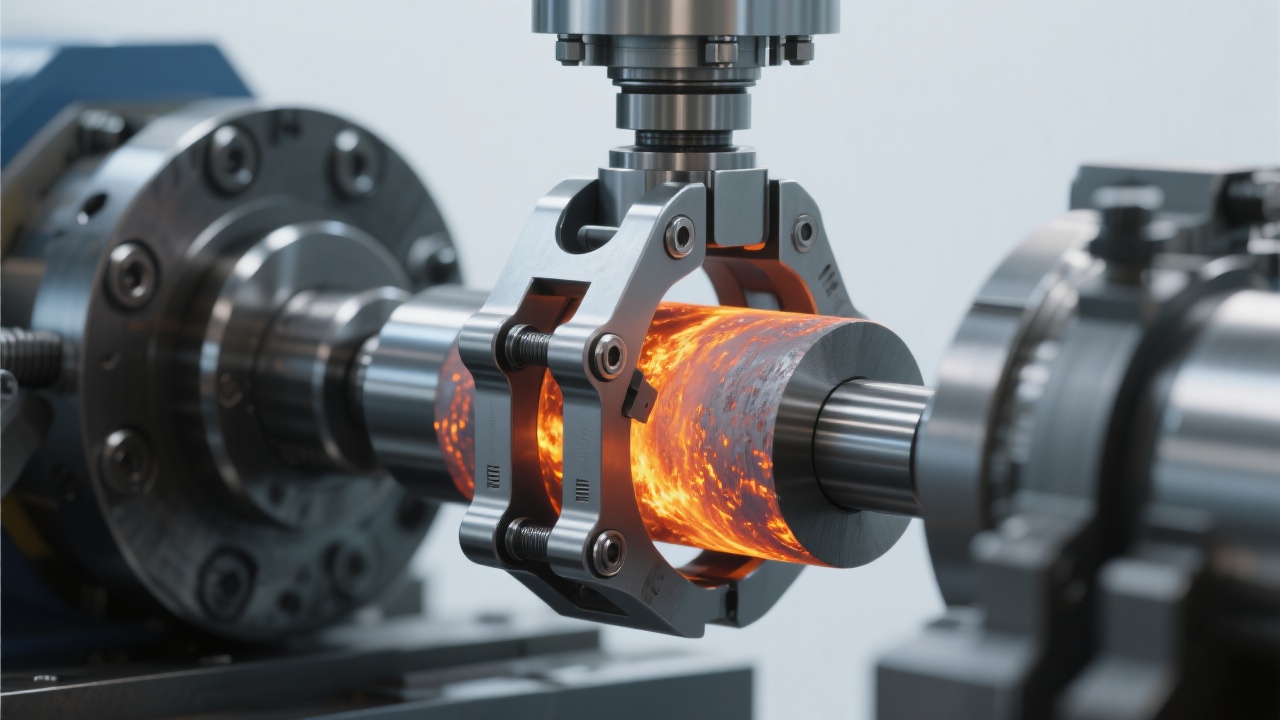

Future trends point towards integrating IoT-enabled diagnostics embedded within clamps to monitor real-time stress, temperature, and wear indicators — transforming maintenance from reactive to predictive. This leap will significantly enhance uptime and operational safety in heavy industries.
Choosing the right steel plate clamp is not just about immediate cost savings but ensuring long-term reliability and safety. These clamps bring:

Ready to elevate your steel transportation safety and efficiency? Discover how our power-driven steel plate clamps can transform your operations.
Have you encountered challenges with steel plate handling in your sector? Share your specific scenarios with us — we’ll provide you with tailored case studies and proven solutions to help you overcome your operational hurdles.

